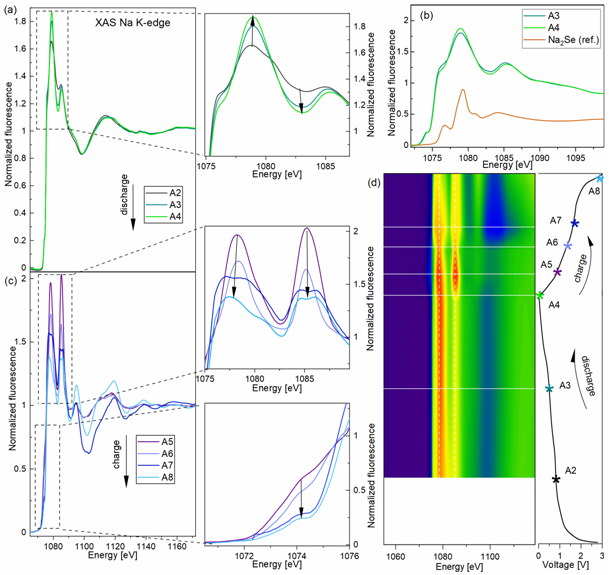
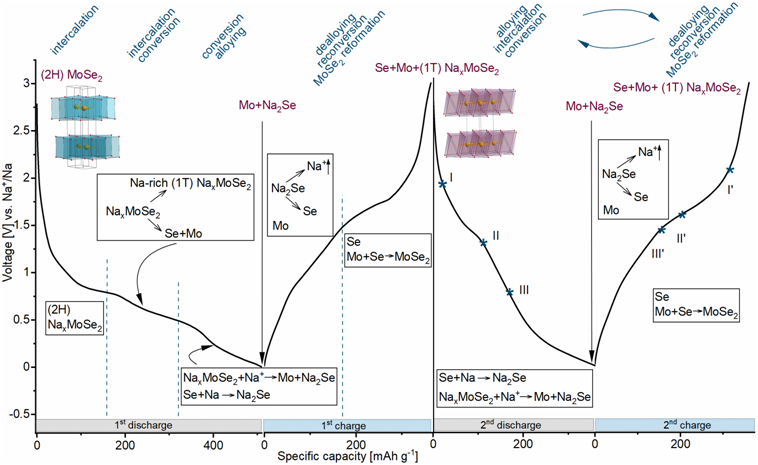
The Na (de)insertion reactions in these kind of compounds can proceed via one of the following routes: intercalation, conversion or alloying. Apparently, we found thatMoSe2 electrode operates via anomalous mutli-way mechanism where Na (de)insertion reaction proceeds sequentially via all three scenarios. By combination of variety operando and ex-situ XRD and XAS studies we observed unexpected phenomena of Se precipitation which leads to the additional alloying reaction.